Is Atp An Organic Molecule
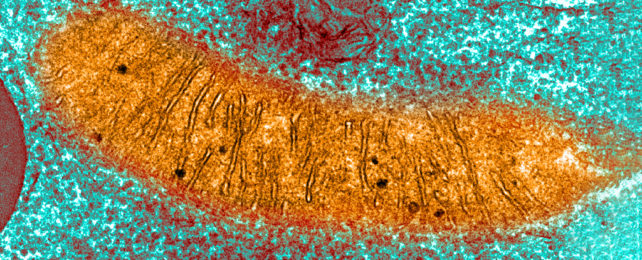 TEM of a mitochondria (believed to exist of leaner origin), where ATP product takes place in animal cells. (Callista Images/Paradigm Source/Getty Images)
TEM of a mitochondria (believed to exist of leaner origin), where ATP product takes place in animal cells. (Callista Images/Paradigm Source/Getty Images)
All life as nosotros know it uses the verbal same energy-carrying molecule as a kind of 'universal cellular fuel'. Now, ancient chemistry may explain how that all-of import molecule ended upwards being ATP (adenosine triphosphate) a new report reports.
ATP is an organic molecule, charged up past photosynthesis or by cellular respiration (the way organisms break down food) and used in every single cell. Every day, we recycle our own torso weight in ATP.
In both the above systems, a phosphate molecule is added to ADP (adenosine diphosphate) through a reaction called phosphorylation – resulting in ATP.
Reactions that release that same phosphate (in another process called hydrolysis) provide chemical energy that our cells apply for countless processes, from encephalon signaling to movement and reproduction.
How ATP ascended to metabolic dominance, in identify of many possible equivalents, has been a long-continuing mystery in biological science and the focus of the research.
"Our results suggest… that the emergence of ATP as the universal energy currency of the cell was non the result of a 'frozen blow'," but arose from unique interactions of phosphorylation molecules, explains evolutionary biochemist Nick Lane from University College London (UCL).
The fact that ATP is used by all living things suggests information technology has been around since life's very beginning and fifty-fifty before, during the prebiotic atmospheric condition that preceded all u.s. breathing matter.
Just researchers are puzzled as to how this could be the case when ATP has such a complicated structure that involves six unlike phosphorylation reactions and a whole lot of energy to create it from scratch.
"There is zilch particularly special about the 'high-energy' [phosphorus] bonds in ATP," says biochemist Silvana Pinna who was with UCL at the time, and colleagues in their paper.
But every bit ATP as well helps build our cells' genetic information, it may accept been roped in for energy use through this other pathway, they annotation.
Pinna and team doubtable another molecules must have been involved initially in the complicated phosphorylation process. So they took a close look at another phosphorylating molecule, AcP, that'due south however used past bacteria and archaea in their metabolism of chemicals, including phosphate and thioester – a chemical thought to accept been abundant at the beginning of life.
In the presence of iron ions (Fe3+), AcP can phosphorylate ADP to ATP in water. Upon testing the ability of other ions and minerals to catalyze ATP formation in water, the researchers could not replicate this with other substitute metals or phosphorylating molecules.
"It was very surprising to discover the reaction is so selective – in the metal ion, phosphate donor, and substrate – with molecules that life still uses," says Pinna.
"The fact that this happens best in h2o under mild, life-compatible conditions is actually quite significant for the origin of life."
This suggests that with AcP, these energy-storing reactions could have place in prebiotic weather, earlier biological life was there to hoard and spur the now self-perpetuating cycle of ATP production.
Furthermore, the experiments suggest that the cosmos of prebiotic ATP was about likely to accept place in freshwater, where photochemical reactions and volcanic eruptions, for example, could provide the right mix of ingredients, the team explains.
While this doesn't completely preclude its occurrence in the ocean, it does hint that the birth of life may have required a strong link to land, they annotation.
"Our results suggest that ATP became established as the universal energy currency in a prebiotic, monomeric earth, on the ground of its unusual chemistry in water," Pinna and colleagues write.
What'due south more, pH gradients in hydrothermal systems could have created an uneven ratio of ATP to ADP, enabling ATP to drive work even in the prebiotic globe of pocket-size molecules.
"Over time, with the emergence of suitable catalysts, ATP could eventually displace AcP as a ubiquitous phosphate donor, and promote the polymerization of amino acids and nucleotides to form RNA, DNA, and proteins," explains Lane.
This enquiry was published in PLOS Biology.
Is Atp An Organic Molecule,
Source: https://www.sciencealert.com/every-life-form-on-earth-uses-the-same-chemical-for-energy-this-could-explain-why
Posted by: folsehishey.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Is Atp An Organic Molecule"
Post a Comment