How To Use Recursion In Java
What is Recursion?
The process in which a function calls itself directly or indirectly is called recursion and the respective function is chosen equally recursive function. Using recursive algorithm, certain problems can exist solved quite easily. Examples of such problems are Towers of Hanoi (TOH), Inorder/Preorder/Postorder Tree Traversals, DFS of Graph, etc.
What is base condition in recursion?
In the recursive program, the solution to the base of operations instance is provided and the solution of the bigger problem is expressed in terms of smaller problems.
int fact(int n) { if (n < = 1) // base example render 1; else render n*fact(n-1); } In the above example, base example for n < = 1 is defined and larger value of number can be solved by converting to smaller ane till base case is reached.
How a particular problem is solved using recursion?
The idea is to represent a trouble in terms of ane or more smaller problems, and add together one or more than base conditions that finish the recursion. For example, nosotros compute factorial northward if we know factorial of (n-1). The base case for factorial would exist n = 0. We return ane when northward = 0.
Why Stack Overflow error occurs in recursion?
If the base instance is not reached or not defined, then the stack overflow problem may arise. Let us accept an instance to sympathize this.
int fact(int n) { // wrong base case (it may crusade // stack overflow). if (n == 100) return 1; else return due north*fact(n-ane); } If fact(x) is chosen, it volition call fact(9), fact(8), fact(7) and so on but the number will never reach 100. Then, the base case is non reached. If the retentivity is exhausted by these functions on the stack, it will cause a stack overflow error.
What is the departure between straight and indirect recursion?
A function fun is called direct recursive if information technology calls the aforementioned function fun. A function fun is called indirect recursive if information technology calls another role say fun_new and fun_new calls fun straight or indirectly. Difference between direct and indirect recursion has been illustrated in Tabular array 1.
- Direct recursion:
void directRecFun() { // Some code.... directRecFun(); // Some code... } - Indirect recursion:
void indirectRecFun1() { // Some lawmaking... indirectRecFun2(); // Some lawmaking... } void indirectRecFun2() { // Some code... indirectRecFun1(); // Some code... }
What is departure between tailed and non-tailed recursion?
A recursive function is tail recursive when recursive phone call is the last thing executed past the function. Please refer tail recursion article for details.
How retention is allocated to different office calls in recursion?
When any office is called from main(), the retentiveness is allocated to information technology on the stack. A recursive function calls itself, the memory for the called function is allocated on peak of retentivity allocated to calling function and different copy of local variables is created for each function call. When the base instance is reached, the office returns its value to the function by whom information technology is called and memory is de-allocated and the process continues.
Let united states of america have the example of how recursion works by taking a simple office.
class GFG {
static void printFun( int test)
{
if (test < i )
return ;
else {
System.out.printf( "%d " , test);
printFun(examination - one );
System.out.printf( "%d " , exam);
render ;
}
}
public static void main(Cord[] args)
{
int test = 3 ;
printFun(test);
}
}
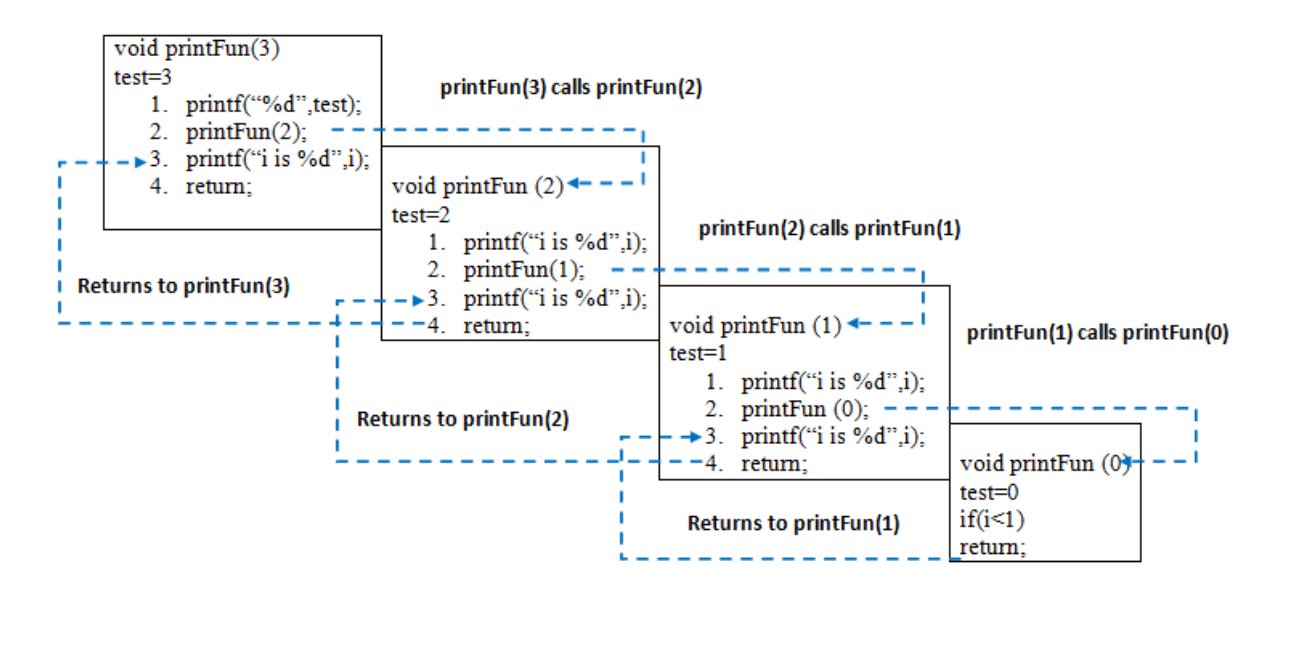
When printFun(three) is called from main(), memory is allocated to printFun(3) and a local variable test is initialized to 3 and statement 1 to four are pushed on the stack as shown in below diagram. It commencement prints '3'. In statement 2, printFun(2) is chosen and retention is allocated to printFun(ii) and a local variable test is initialized to ii and statement 1 to 4 are pushed in the stack. Similarly, printFun(2) calls printFun(i) and printFun(i) calls printFun(0). printFun(0) goes to if statement and it render to printFun(1). Remaining statements of printFun(1) are executed and it returns to printFun(2) and so on. In the output, value from three to 1 are printed and so 1 to three are printed. The memory stack has been shown in below diagram.
What are the disadvantages of recursive programming over iterative programming?
Notation that both recursive and iterative programs take the same problem-solving powers, i.due east., every recursive programme tin can be written iteratively and vice versa is too true. The recursive programme has greater space requirements than iterative program as all functions will remain in the stack until the base case is reached. It also has greater time requirements because of function calls and returns overhead.
What are the advantages of recursive programming over iterative programming?
Recursion provides a clean and uncomplicated manner to write code. Some problems are inherently recursive similar tree traversals, Tower of Hanoi, etc. For such problems, it is preferred to write recursive lawmaking. We can write such codes also iteratively with the assist of a stack data structure. For instance refer Inorder Tree Traversal without Recursion, Iterative Belfry of Hanoi.
How To Use Recursion In Java,
Source: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/recursion-in-java/
Posted by: folsehishey.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How To Use Recursion In Java"
Post a Comment